Lung Cancer – Causes and Symptoms
According to the World Health Organization, lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide, with more than 1.8 million new cases diagnosed each year. It’s estimated that one person dies of lung cancer every 30 seconds. The burden of lung cancer is greatest in low- and middle-income countries, where most cases are diagnosed at a late stage when treatment is less likely to be effective.
Do you smoke?
Every individual who smokes claims to find solace in smoking. Some claim they are only able to think well when smoking. Some claim smoking helps them forget about the harsh treatments of life. Whatever your reason for smoking is, always ensure to clean after you. Everytime you puff on that cigarette, your lungs feel the impact hence, it’s important to get rid of the chemicals that put your lungs at risk of cancer due to smoking and stay safe from lung cancer.
Click here to order for fekomi Idan gan gan to get rid of nicotine in your lungs.
What is lung cancer?
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the lungs. The lungs are a pair of organs in the chest that allow us to breathe by taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. The lungs are made up of several different types of cells, and it can start in any of these cells.
They are made up of two main parts: the bronchi and the alveoli. The bronchi are the large airways that carry air to and from the lungs. The alveoli are tiny air sacs at the ends of the bronchi where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged.
Most lung cancers start in the bronchi or the alveoli. Some start in other parts of the lungs, such as the bronchioles (small airways) or the pleura (lining of the lungs).
The way it forms depends on the type of cells it starts in. There are two main types of lung cells: epithelial cells and mesothelial cells. Epithelial cells line the bronchi, alveoli, and other parts of the lungs. Mesothelial cells line the pleura. Most lung cancers start in the epithelial cells. As the cells become damaged, they can start to divide uncontrollably and form a tumor. This process can take many years, and it often starts with a precancerous condition called dysplasia. Dysplasia is when the cells start to look abnormal
What happens if dysplasia is not treated?
If dysplasia is not treated, it can eventually progress to a type of cancer called carcinoma in situ. Carcinoma in situ is cancer that hasn’t spread beyond the original cells. If it is left untreated, it can eventually turn into invasive cancer, which is cancer that has spread to other parts of the body. Lung cancer can also spread through the lymphatic system. This is a network of vessels and glands that help fight infection. The lymphatic system drains into the lungs, so cancer cells can travel from the lungs to other parts of the body.
Symptoms of lung cancer
Some people with lung cancer don’t have any symptoms in the early stages. When symptoms do appear, they can vary depending on the type and location of the cancer. Some common symptoms of lung cancer include:
- A cough that doesn’t go away
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Coughing up blood
- Hoarseness
- Swelling in the face or neck
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Headaches
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, see a doctor right away. While these symptoms can be caused by other conditions, it’s still important to see a doctor to rule out the possibility of lung cancer.
People with this type of cancer may also experience symptoms related to the spread of the cancer, such as bone pain, seizures, and jaundice. These symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, so it’s important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
Causes of lung cancer
There are many possible causes of lung cancer, but the most common cause is smoking. In fact, about 80-90% of lung cancer cases are caused by smoking. Read about effects
Other risk factors for lung cancer include:
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
- Exposure to radon gas
- Exposure to asbestos
- Having a family history
- Also, there are some genetic mutations that can increase a person’s risk of developing lung cancer. These mutations include EGFR mutations, ALK mutations, and KRAS mutations.
Risk factors for developing lung cancer
The most important risk factor is smoking, which accounts for about 90% of lung cancer cases. Other risk factors include exposure to secondhand smoke, exposure to radon gas, and occupational exposure to carcinogens. Additionally, a family history of lung cancer can increase a person’s risk.
Types of lung cancer
There are two main types:
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
NSCLC is the more common type, accounting for about 85% of all lung cancer cases. NSCLC can be further divided into three subtypes: adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
SCLC is less common, accounting for about 10-15% of lung cancer cases. It tends to be more aggressive than NSCLC and is more likely to spread to other parts of the body.
SCLC is highly sensitive to chemotherapy and radiation therapy. This means that treatment can often shrink or eliminate the tumor. However, SCLC is also more likely to recur after treatment. This is one of the reasons why SCLC has a poor prognosis.
On the other hand, NSCLC is less likely to respond to treatment, but it has a better prognosis overall.
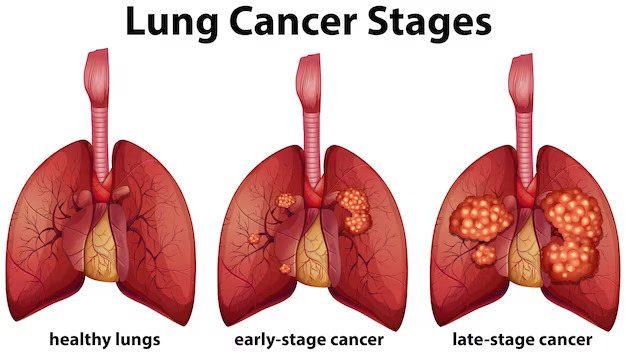
Stages
The stages of lung cancer are numbered from I to IV.
Stage 0: the cancer is limited to the surface of the lungs and has not invaded deeper tissue. It is sometimes also called “carcinoma in situ” or CIS.
Stage I: earliest stage with a small tumor that has not spread to any lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
For stage II: the tumor is larger or has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Stage III: tumor is larger or has spread to nearby lymph nodes and other tissues or organs in the chest.
Stage IV: this is the most advanced stage and means the tumor has spread to other parts of the body.
Each stage is then divided into sub-stages (such as IIA or IIIB).
How to diagnose lung cancer
To diagnose lung cancer, doctors typically start by taking a medical history and conducting a physical exam. If there are signs, the next step is usually imaging tests like a chest X-ray or CT scan. These tests can show whether there are any abnormal masses or areas of inflammation in the lungs. If an abnormality is found, the next step is usually a biopsy. A biopsy involves taking a small sample of tissue from the lung and examining it under a microscope to look for cancer cells.
Treatment options
The treatment options vary depending on the type and stage of the cancer.
For early-stage, surgery is often the first-line treatment. This involves removing the tumor and a small amount of healthy tissue around it.
If the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are often used. These treatments can shrink tumors and slow the spread of the cancer.
In some cases, immunotherapy may also be used. This is a treatment that uses the body’s own immune system to fight cancer.
Side effects
The side effects of the treatment can vary depending on the type of treatment, but some common ones include fatigue, hair loss, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These side effects are usually temporary and can be managed with medications. In some cases, patients may also experience long-term side effects, such as lung damage from radiation therapy or infertility from chemotherapy. It’s important to talk to your doctor about the possible side effects of treatment and how they can be managed.
Prognosis
The prognosis varies depending on the stage of the cancer and other factors like the patient’s age and overall health. Generally, the earlier the cancer is diagnosed, the better the prognosis is.
For stage I lung cancer, the five-year survival rate is about 60-80%.
Stage II lung cancer, the five-year survival rate is about 35-55%.
For stage III, the five-year survival rate is about 15-25%.
For stage IV lung cancer, the five-year survival rate is about 5%.
Prognosis can also vary based on the patient’s response to treatment.
Your Wellness Is Our Concern At Fekomi Wellness
Are you suffering from sexual dysfunctions such as erectile dysfunction, premature (delayed) ejaculation, and low libido? Fekomiherbals has the ultimate solution.
Also, our team of highly qualified and certified healthcare consultants at Fekomi wellness are always ready and happy to help you with your health concerns. Visit Fekomi wellness today to book an appointment and get started on your health journey. Kindly call our desk line on +2349074197154 for more enquiries.
